Electrical Stimulation Therapy (E-Stim) is a therapeutic technique commonly used in rehabilitation and pain management to alleviate discomfort, promote tissue healing, and improve muscle function. This therapy involves the application of controlled electrical impulses to specific areas of the body via electrodes attached to the skin’s surface. E-Stim comes in various forms, including transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for pain relief, neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) for muscle rehabilitation, and interferential current (IFC) therapy for deeper tissue penetration.
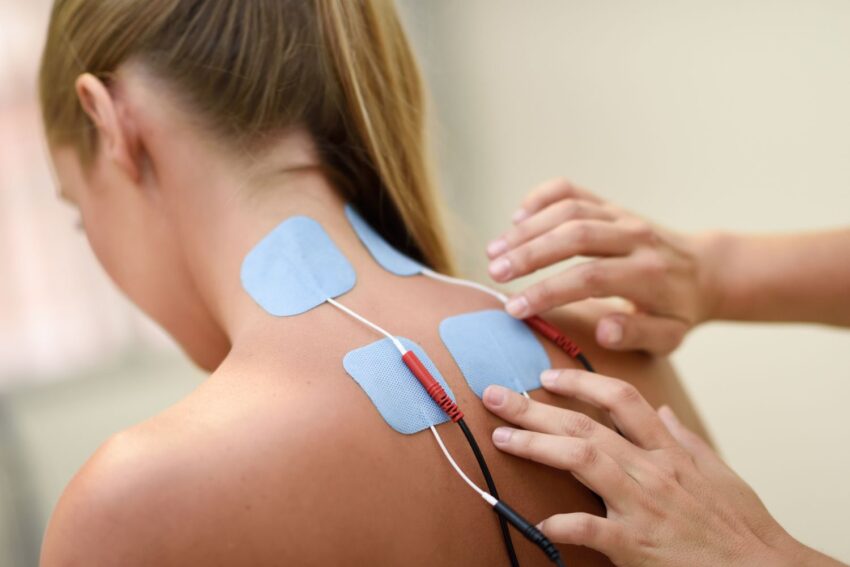
How does it work?
E-Stim functions by delivering mild electrical currents to targeted areas, modulating nerve activity and muscle contractions. With TENS, low-frequency electrical impulses block pain signals from reaching the brain, providing relief from various types of acute or chronic pain. NMES, on the other hand, aims to stimulate weakened or atrophied muscles, facilitating muscle contraction and strengthening. Through this stimulation, E-Stim can also trigger the release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers, aiding in pain reduction and promoting a sense of well-being.
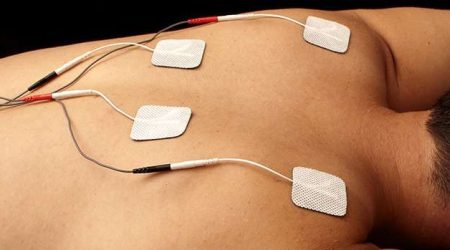
Benefits of E-Stim Therapy
The benefits of E-Stim therapy are diverse and depend on the specific type and application. This modality effectively manages pain by either blocking pain signals or triggering the release of endorphins, providing a non-invasive alternative for pain relief. Additionally, E-Stim aids in muscle rehabilitation by stimulating contractions, preventing muscle atrophy, and promoting tissue repair, making it beneficial for individuals recovering from injuries or surgeries. Furthermore, this therapy helps improve blood circulation, reduce swelling, and enhance range of motion, contributing to overall functional improvement and supporting the body’s healing process.
